Securing Entra ID Administration: Tier 0

Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) is the core service upon which Microsoft 365 applications rely for directory and authentication services. This makes Entra ID security a critical element for any organization that leverages Microsoft 365 services. The most important component in Entra ID security is administration, and this blog covers the key concepts around securing the most privileged accounts in Entra ID, which are considered Tier 0.
The term Tier 0 was coined by Microsoft to identify assets, roles, and accounts that are considered the most privileged and therefore require the most protection. Tier 0 refers to the inner ring of protected assets.
1. Focus on the key Entra ID roles that are considered Tier 0.
To start this journey, it is important to identify what needs to be protected. As the most privileged of all, Tier 0 roles require additional scrutiny.
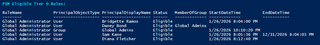
In this TrustedSec blog, the following nine (9) roles are identified as Tier 0:
|
|
The Application Administrator and Cloud Application Administrator roles have full control over applications, which is important when there are highly privileged applications in the environment. Conditional Access Administrator can modify Conditional Access policies, which can dramatically change the security posture of the tenant. The Global Administrator role is the most powerful of all and should ideally be limited to three (3) to five (5) members. Where possible, use a combination of roles instead of Global Administrator.
The Hybrid Identity Administrator role can control federation and other hybrid cloud configurations, which makes it a powerful role. Microsoft states that Partner Tier2 Support should not be used; it was designated for a specific use case but is no longer needed. Privileged Authentication Administrator can control authentication for highly privileged roles like Global Administrator, and Privileged Role Administrator can manage role membership, including Global Administrator. Finally, Security Administrator controls sensitive security configurations.
Focusing on these first will make it easier to secure Entra ID administration more quickly.
2. Review membership of Tier 0 roles.
Now that we have identified what roles require a high level of protection, it’s necessary to determine which accounts have the highest level of rights in the environment. Reviewing the membership of the Tier 0 roles is necessary to validate that they should have highly privileged rights. Membership should only include dedicated administrative accounts, preferably accounts that have additional protection.
Tier 0 accounts must have clear naming standards so automation can check for any accounts that don’t belong. For example, T0-JSmith is useful to quickly identify if the account should be a member of Tier 0.
3. Review Privileged Identity Management (PIM) eligible members of Tier 0 roles, if applicable.
For a full view of all Tier 0 members, it’s necessary to also review the accounts and groups that are PIM eligible for Tier 0 roles (when PIM is in use). These eligible accounts can elevate to be an active member in the configured role(s).
All Tier 0 membership must be PIM eligible instead of permanently active when PIM is use. Most of the tenants TrustedSec assesses as part of our Entra ID security assessments are predominantly configured with permanent membership, even when using PIM.
Note that there are some rare exceptions to this such as emergency break glass accounts and certain service accounts.
PIM provides numerous benefits such as privilege usage tracking, just-in-time privileges, gated privileges where rights are only granted when approved by another person, and more.
4. Review Role Assignable Groups that are members of Tier 0 roles, if applicable.
Role Assignable Groups are created and configured to be members of Entra ID role(s). This nested group membership makes enumerating full membership of Tier 0 roles more challenging because reviews of role and group memberships are necessary (which requires reviewing the group membership separately). Furthermore, an owner of a Role Assignable Group can modify the group membership, so anyone with owner rights of a group that is a member of a Tier 0 role needs to be captured as a potential Tier 0 role member.
For example, the Global Administrator role has a Role Assignable Group that is a member called Global Admins and John Smith is an owner of that group. This means that John Smith can modify the Global Admins group membership, which controls who can be a member of the Tier 0 role Global Administrator. In this case, John Smith needs to be considered a potential Global Administrator.
5. Ensure proper licensing is configured.
In the cloud, it is often the case that additional licensing is required for security capability. In order to leverage Conditional Access, Entra ID P1 is required, while Entra ID P2 is required for PIM. All Tier 0 accounts should be licensed at the P2 level to leverage PIM for just-in-time administration.
6. Ensure that all accounts that are members of these Tier 0 roles or are PIM eligible are using cloud-only admin accounts and not standard user accounts.
Standard user accounts are used for web browsing, email, and Office applications. They should not have any elevated privileges. Regular reviews of highly privileged role membership ensure that standard user accounts are not being used for administrative tasks.
Any accounts that don’t belong should be removed. There should be no shared, generic admin accounts that are members of Tier 0 roles; these are accounts named something like “Admin” with no clear owner or record of use. Any standard user accounts that are members should be removed and replaced with admin accounts. Membership of service accounts and service principals should be scrutinized.
Note that accounts that are members of Tier 0 roles must be cloud-only accounts and not synchronized from the on-premises Active Directory (AD) environment.
7. Ensure there is a Conditional Access policy that always requires multi-factor authentication (MFA) and logon restrictions for membership of Tier 0 roles.
Conditional Access provides the capability to require additional security controls during the authentication process, such as MFA. Conditional Access must be leveraged to ensure that human accounts that are members of Tier 0 roles are required to use MFA for every authentication.
FIDO2 MFA is resistant to phishing and Adversary-in-the-Middle (AITM) attacks and should be required for Tier 0 roles. The best way to configure the Conditional Access policy is to target the list of Tier 0 roles (above) and require the use of Microsoft Authenticator push notification with number matching or FIDO2 keys. This limits impact when password-spray attacks are performed against the tenant.
Furthermore, Conditional Access policy should restrict where Tier 0 accounts can log on, which is especially important for service accounts. The Conditional Access policy can leverage Named Locations to ensure authentication only occurs in a specific network address range or even a specific IP address.
8. Ensure Tier 0 accounts that perform administration leverage an admin system.
A user will log on through the web browser to the cloud environment using cloud credentials. Attackers are able to extract the bearer token, often stored as a cookie or token, from the web browser. With this token, attackers can impersonate the signed in cloud admin for a period of time. The best security for Entra ID tenant administration (Tier 0 activity) is a separate computer, aka a privileged access workstation (PAW), since the token is protected from capture.
Good: A second web browser is only used for cloud administrative tasks.
Better: An admin server is accessed via RDP to perform administrative tasks.
Best: An entirely separate computer is used for administrative tasks.
9. Create and maintain two (2) emergency break glass accounts.
Microsoft strongly recommends creating two (2) emergency break glass accounts that can be used if other admins are locked out. The emergency accounts should be excluded from Conditional Access requirements and be permanent members of the Global Administrator role. TrustedSec recommends configuring a FIDO2 key for each emergency account and keeping the FIDO2 keys in the safe. Monitor the emergency accounts for any unexpected logon.
Reference: Manage emergency access accounts in Microsoft Entra ID
10. Set a schedule to review Tier 0 role membership.
Now that we have reviewed membership, ensured that cloud-only admin accounts are members, and configured phishing-resistant MFA enforcement for these role members, the next step is to set a schedule for review.
This review should occur every three (3) months or once a quarter (at a minimum).
PowerShell Script for Reviewing Tier 0 Role Membership
To make identifying privileged accounts in Tier 0 roles easier, I wrote the PowerShell script Get-EntraIDTier0.ps1, which leverages the Entra ID and Graph PowerShell modules.
Use the InstallPreReqs parameter to install the required PowerShell modules.